Jakarta, Indonesia’s capital city, faces critical challenges from land subsidence and flooding that have intensified in recent decades. The metropolitan area, which houses over ten million people, sits on a low-lying coastal plain that makes it susceptible to both sea level rise and ground subsidence. Current subsidence rates reach up to 25 centimeters per year in certain districts, primarily caused by excessive groundwater pumping and natural soil compaction.
These conditions create substantial risks to urban infrastructure, economic activities, and public safety. The city’s geographic position and tropical climate compound these challenges. During monsoon periods, Jakarta receives heavy precipitation that overwhelms drainage systems already compromised by subsiding land.
The interaction between ground subsidence and seasonal rainfall patterns results in frequent flooding events that disrupt transportation, commerce, and residential areas. The combination of these factors has created an urgent need for comprehensive flood management and subsidence mitigation strategies to protect the city’s population and economic assets.
Key Takeaways
- Jakarta is facing a severe crisis of land subsidence and frequent flooding, threatening the city’s stability.
- Subsidence has caused significant damage to infrastructure, worsening the city’s vulnerability to floods.
- Climate change intensifies flooding by increasing rainfall and sea level rise, compounding Jakarta’s challenges.
- Government initiatives are underway to combat subsidence and flooding, but solutions require comprehensive planning.
- The crisis has profound economic, social, and environmental impacts, affecting communities and the city’s future sustainability.
The impact of subsidence on Jakarta’s infrastructure
The infrastructure of Jakarta is under immense strain due to the ongoing subsidence crisis. Roads, bridges, and public transportation systems are increasingly vulnerable to damage from flooding and land sinking. Many of the city’s vital transport routes have become impassable during heavy rains, leading to significant disruptions in mobility for residents and commuters alike.
The deterioration of infrastructure not only hampers daily activities but also poses serious risks to public safety. Emergency services often struggle to reach those in need during flooding events, highlighting the urgent need for resilient infrastructure that can withstand these challenges. Moreover, the impact of subsidence extends beyond transportation.
Essential services such as water supply, sanitation, and electricity are also affected. Flooding can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to contamination of drinking water sources and increased health risks for the population. The degradation of infrastructure has far-reaching consequences for economic activities as well; businesses face interruptions due to flooding, which can lead to financial losses and reduced productivity.
As Jakarta continues to grapple with these issues, it becomes increasingly clear that addressing subsidence is critical for ensuring the functionality and safety of the city’s infrastructure.
The role of climate change in exacerbating Jakarta’s flooding
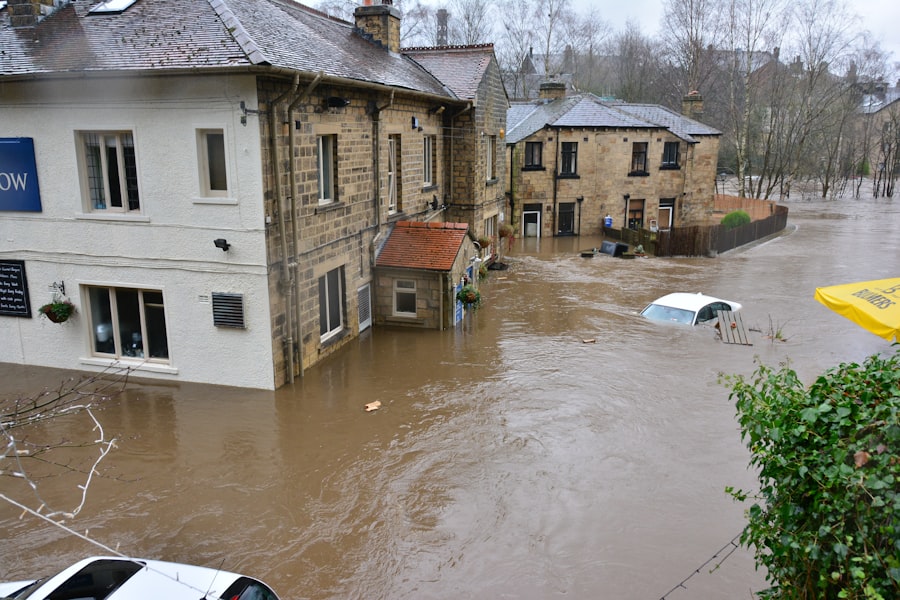

Climate change plays a pivotal role in exacerbating Jakarta’s flooding crisis. Rising global temperatures have led to increased sea levels, which pose a significant threat to coastal cities like Jakarta. As sea levels rise, the risk of coastal flooding intensifies, particularly in areas already experiencing subsidence.
The combination of these two factors creates a precarious situation for Jakarta, where even minor weather events can result in catastrophic flooding. Additionally, climate change has altered rainfall patterns, leading to more intense and unpredictable monsoon seasons that further strain the city’s drainage systems. The implications of climate change extend beyond immediate flooding concerns; they also threaten long-term sustainability.
As Jakarta continues to experience extreme weather events, the city’s ability to adapt becomes increasingly challenged. Urban planners and policymakers must consider climate resilience in their strategies to combat flooding and subsidence. Failure to address these issues could result in irreversible damage to both the environment and the livelihoods of millions of residents who depend on Jakarta’s resources.
The government’s efforts to address Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding
In response to the escalating crisis, the Indonesian government has initiated various efforts aimed at mitigating Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding challenges. One significant measure has been the implementation of a comprehensive flood management plan that includes improving drainage systems and constructing retention basins to manage excess rainwater. These initiatives are designed to enhance the city’s capacity to cope with heavy rainfall and reduce the risk of flooding in vulnerable areas.
Additionally, the government has recognized the need for stricter regulations on groundwater extraction, which is a primary driver of subsidence. Efforts are underway to promote sustainable water management practices and encourage the use of alternative water sources. However, despite these initiatives, challenges remain in terms of funding, coordination among various government agencies, and public awareness.
The complexity of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis necessitates a multifaceted approach that involves collaboration between local communities, government bodies, and international organizations.
The economic costs of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding
| Metric | Value | Unit | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Annual Land Subsidence Rate | 7.5 | cm/year | Varies across different parts of Jakarta |
| Maximum Recorded Subsidence | 28 | cm/year | In northern Jakarta areas |
| Percentage of Jakarta Below Sea Level | 40 | % | Due to subsidence and sea level rise |
| Annual Flooded Area | 300 | km² | Estimated area affected by flooding annually |
| Population Affected by Flooding | 5 | million people | Residents impacted by subsidence-related floods |
| Groundwater Extraction Rate | 2,000 | million liters/day | Major cause of land subsidence |
| Sea Level Rise Rate | 3.4 | mm/year | Contributes to increased flooding risk |
The economic ramifications of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis are profound and far-reaching. The city incurs substantial costs related to disaster response and recovery efforts each year. Flooding events disrupt businesses, leading to lost revenue and increased operational costs for companies forced to deal with damaged infrastructure or interrupted supply chains.
Furthermore, property values in flood-prone areas have declined significantly, impacting homeowners and investors alike. The long-term economic implications are equally concerning. As Jakarta continues to sink and flood, potential investors may be deterred from establishing businesses in the city due to perceived risks associated with environmental instability.
This could stifle economic growth and limit job opportunities for residents. Additionally, the costs associated with repairing infrastructure and implementing flood mitigation measures can strain government budgets, diverting funds from other essential services such as education and healthcare. Addressing these economic challenges is crucial for ensuring Jakarta’s resilience in the face of ongoing environmental threats.
The social and human impact of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding

The social consequences of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis are deeply felt among its residents. Communities living in low-lying areas are particularly vulnerable to flooding, often facing displacement during severe weather events. The psychological toll on affected individuals can be significant; families may lose their homes and possessions, leading to feelings of insecurity and anxiety about their future.
Moreover, access to basic services such as healthcare and education can be severely disrupted during flooding events, exacerbating existing inequalities within the city. The human impact extends beyond immediate physical displacement; it also affects social cohesion within communities. As families are forced to relocate or seek refuge in temporary shelters, traditional support networks may be disrupted.
This can lead to increased social tensions as resources become scarce and competition for aid intensifies. Addressing these social challenges requires not only immediate disaster response efforts but also long-term strategies aimed at building community resilience and fostering social solidarity among residents.
The potential solutions to Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis
Finding effective solutions to Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both immediate needs and long-term sustainability. One potential solution involves investing in green infrastructure, such as parks and green roofs, which can help absorb rainwater and reduce surface runoff during heavy rainfall events. These initiatives not only mitigate flooding but also enhance urban biodiversity and improve air quality.
Another promising avenue is the promotion of sustainable urban planning practices that prioritize resilience against climate change impacts. This includes implementing zoning regulations that discourage development in flood-prone areas while encouraging investment in infrastructure improvements in vulnerable neighborhoods. Additionally, raising public awareness about water conservation practices can help reduce groundwater extraction rates, ultimately contributing to stabilizing land levels in affected areas.
The role of urban development in Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding
Urban development plays a critical role in both exacerbating and potentially alleviating Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis. Rapid urbanization has led to increased demand for land and resources, often resulting in unregulated construction practices that compromise natural drainage systems. As concrete surfaces replace green spaces, rainwater runoff increases, overwhelming existing drainage infrastructure during heavy rains.
However, urban development also presents opportunities for innovative solutions that can mitigate these challenges. By integrating sustainable design principles into new construction projects, developers can create spaces that enhance resilience against flooding while promoting environmental sustainability. For instance, incorporating permeable materials in roadways or creating retention ponds can help manage stormwater effectively while reducing pressure on drainage systems.
The environmental consequences of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding
The environmental consequences of Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis are profound and multifaceted. As land sinks and floods become more frequent, ecosystems within the region face significant disruption. Wetlands that once served as natural buffers against flooding are being lost due to urban encroachment and pollution from runoff.
This loss not only diminishes biodiversity but also reduces the city’s capacity to manage stormwater effectively. Moreover, pollution from flooded areas poses serious risks to both human health and local ecosystems. Contaminated water sources can lead to outbreaks of waterborne diseases among residents while harming aquatic life in nearby rivers and coastal areas.
Addressing these environmental challenges requires a holistic approach that prioritizes ecosystem restoration alongside urban development efforts.
The community response to Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis
Community response plays a vital role in addressing Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis. Local organizations have emerged as key players in advocating for sustainable practices while providing support for affected residents during flooding events. Grassroots initiatives focused on community education about disaster preparedness have gained traction, empowering residents with knowledge about how to respond effectively during emergencies.
Additionally, community-led efforts aimed at restoring local ecosystems have shown promise in enhancing resilience against flooding.
The future outlook for Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis
The future outlook for Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis remains uncertain but not without hope. While challenges persist due to ongoing urbanization pressures and climate change impacts, there is growing recognition among stakeholders about the need for collaborative action. Policymakers are increasingly prioritizing sustainable development practices that consider environmental resilience alongside economic growth.
Furthermore, advancements in technology offer new possibilities for monitoring land subsidence patterns more accurately while improving flood prediction capabilities through data analytics. By harnessing these tools alongside community engagement efforts, Jakarta has an opportunity to build a more resilient future—one where residents can thrive despite the challenges posed by subsidence and flooding. In conclusion, addressing Jakarta’s subsidence and flooding crisis requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses infrastructure improvements, sustainable urban planning practices, community engagement initiatives, and environmental restoration efforts.
By recognizing the interconnectedness of these issues, stakeholders can work together towards creating a safer and more resilient city for all its inhabitants.
Jakarta, the capital city of Indonesia, is facing severe challenges due to subsidence and flooding, which have been exacerbated by rapid urbanization and climate change. A related article that delves into the implications of these environmental issues can be found at