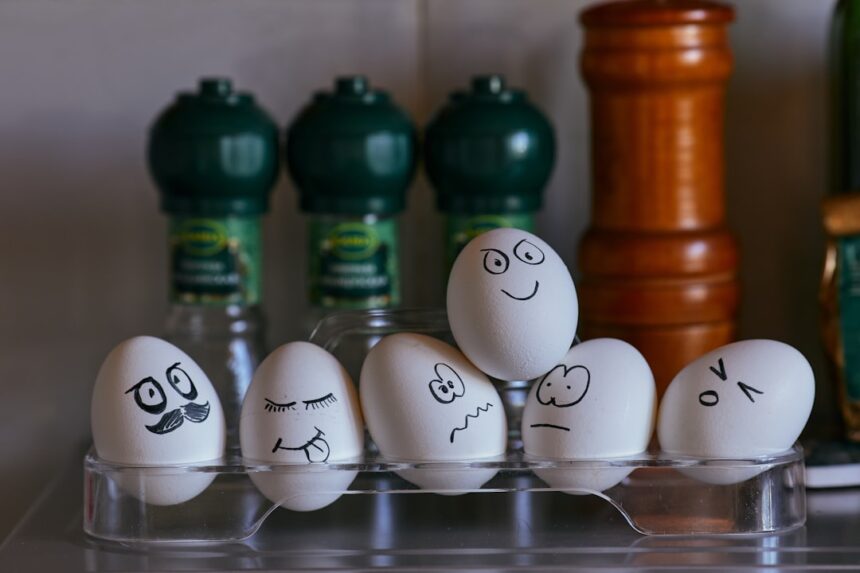
In the intricate landscape of human emotions, the ability to name and articulate feelings plays a crucial role in how you navigate your emotional experiences. Emotion naming, or the process of identifying and labeling your feelings, serves as a foundational skill in emotional intelligence. When you can accurately name your emotions, you gain a clearer understanding of your internal state, which can lead to more effective emotional regulation and interpersonal communication.
This skill is not merely a linguistic exercise; it is deeply intertwined with your psychological well-being and overall mental health. The significance of emotion naming extends beyond personal insight. It influences how you relate to others and how you respond to various situations.
By recognizing and labeling your emotions, you can better manage stress, enhance your relationships, and foster resilience in the face of challenges. As you delve deeper into the science behind emotion naming, you will discover its profound connections to brain function, particularly the role of the amygdala in processing emotions. Understanding these connections can empower you to harness the power of emotion naming in your daily life.
Key Takeaways
- Naming emotions activates the amygdala, a key brain region involved in emotion processing.
- Emotion naming enhances emotional regulation by helping individuals better understand and manage their feelings.
- Incorporating emotion naming in therapy can improve mental health outcomes and reduce anxiety and stress.
- Emotion naming is linked to mindfulness practices and supports social and emotional learning.
- Future research aims to further explore how emotion naming influences amygdala activation and emotion regulation strategies.
The Role of the Amygdala in Emotion Processing
The amygdala, a small almond-shaped cluster of nuclei located deep within the temporal lobes of your brain, plays a pivotal role in how you process emotions. It acts as a key player in the emotional response system, helping you to detect and respond to threats in your environment. When you encounter a stimulus that elicits an emotional reaction—be it fear, joy, or sadness—the amygdala is activated, triggering a cascade of physiological responses that prepare your body to react.
This rapid response system is essential for survival, allowing you to respond quickly to potential dangers. However, the amygdala’s influence extends beyond immediate reactions; it also shapes how you experience and interpret emotions over time. Research has shown that the amygdala is involved in the formation of emotional memories, which can affect how you perceive similar situations in the future.
When you name your emotions, you engage cognitive processes that can modulate the amygdala’s activity. This interplay between emotion and cognition highlights the importance of understanding how naming emotions can impact your emotional experiences and responses.
The Study on Emotion Naming and Amygdala Activation

Recent studies have explored the relationship between emotion naming and amygdala activation, shedding light on how this process can influence your emotional experiences. In one notable study, participants were presented with emotionally charged images while their brain activity was monitored using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The findings revealed that when participants were asked to label their emotions in response to these images, there was a significant reduction in amygdala activation compared to when they simply viewed the images without naming their feelings.
This reduction in amygdala activation suggests that emotion naming may serve as a form of cognitive regulation, allowing you to exert control over your emotional responses. By labeling your feelings, you engage higher-order cognitive processes that can help to dampen the intensity of your emotional reactions. This insight underscores the potential benefits of developing strong emotion-naming skills as a means of enhancing emotional regulation and reducing the impact of negative emotions on your mental state.
The Effect of Emotion Naming on Emotional Regulation
The act of naming your emotions can have profound effects on your ability to regulate them effectively. When you take the time to identify and articulate what you are feeling, you create a space for reflection and understanding. This process allows you to step back from overwhelming emotions and view them from a more objective standpoint.
As a result, you may find it easier to manage intense feelings such as anger, anxiety, or sadness. Moreover, emotion naming can facilitate problem-solving and decision-making. When you clearly identify what you are feeling, you can better assess the situation at hand and determine appropriate responses.
This clarity can lead to healthier coping strategies and more constructive interactions with others. By honing your ability to name your emotions, you empower yourself to navigate life’s challenges with greater resilience and confidence.
The Importance of Emotion Naming in Mental Health
| Study | Participants | Method | Key Finding | Amygdala Activation Reduction (%) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torrisi et al. (2013) | 20 healthy adults | fMRI during emotion labeling vs. passive viewing | Labeling emotions reduced amygdala activation compared to passive viewing | ~30% | Emotion labeling involved naming facial expressions |
| Lieberman et al. (2007) | 15 participants | fMRI during affect labeling task | Amygdala activity decreased when participants named emotions | 25-35% | Supports emotion regulation via labeling |
| Burklund et al. (2014) | 30 adults | fMRI comparing affect labeling and reappraisal | Both strategies reduced amygdala activation; labeling showed significant reduction | 28% | Labeling was as effective as cognitive reappraisal |
| Hariri et al. (2000) | 12 participants | fMRI during emotion matching vs. labeling | Labeling emotions led to decreased amygdala response | ~20% | Early evidence for affect labeling effect |
Emotion naming is not just a useful skill; it is a vital component of mental health and well-being. Research has shown that individuals who struggle with identifying their emotions are at a higher risk for various mental health issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, and emotional dysregulation. When you lack the ability to articulate your feelings, it can lead to confusion and frustration, making it difficult to seek help or communicate effectively with others.
Conversely, those who possess strong emotion-naming skills tend to experience better mental health outcomes. By being able to express their feelings accurately, they are more likely to engage in healthy coping mechanisms and seek support when needed. This connection between emotion naming and mental health highlights the importance of fostering this skill in both personal development and therapeutic settings.
Practical Applications of Emotion Naming in Therapy

In therapeutic contexts, emotion naming is often employed as a powerful tool for facilitating healing and growth. Therapists frequently encourage clients to articulate their feelings as a means of promoting self-awareness and insight. By guiding you through the process of identifying and labeling emotions, therapists can help you uncover underlying issues that may be contributing to distress or dysfunction.
When you are able to express your feelings clearly, it fosters a deeper understanding between you and your therapist.
As such, incorporating emotion naming into therapy can be an invaluable strategy for enhancing emotional awareness and promoting healing.
Implications for Emotion Regulation Strategies
The insights gained from understanding emotion naming and its relationship with the amygdala have significant implications for developing effective emotion regulation strategies. By recognizing the importance of labeling emotions, you can incorporate this practice into your daily life as a means of enhancing emotional awareness and regulation. Simple techniques such as journaling about your feelings or using emotion charts can help you cultivate this skill over time.
Moreover, integrating emotion naming into mindfulness practices can further enhance its effectiveness. Mindfulness encourages present-moment awareness and acceptance of emotions without judgment. By combining mindfulness with emotion naming, you create a powerful synergy that allows for deeper emotional processing and regulation.
This holistic approach can lead to greater emotional resilience and well-being.
The Connection Between Emotion Naming and Mindfulness
Mindfulness practices emphasize awareness of thoughts and feelings without judgment or reactivity. When you engage in mindfulness meditation or other mindfulness exercises, incorporating emotion naming can deepen your practice significantly. By consciously acknowledging and labeling your emotions as they arise during mindfulness sessions, you create an opportunity for greater self-awareness and acceptance.
This connection between emotion naming and mindfulness not only enhances your ability to regulate emotions but also fosters a sense of compassion towards yourself. As you learn to recognize and accept your feelings without judgment, you cultivate a more nurturing relationship with yourself. This compassionate approach can lead to improved mental health outcomes and greater overall well-being.
Emotion Naming in the Context of Social and Emotional Learning
In educational settings, emotion naming is increasingly recognized as an essential component of social and emotional learning (SEL) programs. These programs aim to equip students with the skills necessary for emotional intelligence, interpersonal relationships, and responsible decision-making. By teaching students how to identify and articulate their emotions, educators can foster a supportive environment that promotes emotional well-being.
When students learn to name their emotions effectively, they become better equipped to navigate social interactions and conflicts. This skill not only enhances their ability to communicate but also encourages empathy towards others’ feelings. As students develop strong emotion-naming skills through SEL programs, they are likely to experience improved academic performance and healthier relationships both inside and outside the classroom.
The Potential for Emotion Naming to Reduce Anxiety and Stress
The practice of emotion naming holds significant potential for reducing anxiety and stress levels in individuals. When faced with overwhelming emotions or stressful situations, taking a moment to pause and identify what you are feeling can create a sense of clarity amidst chaos. By labeling your emotions—whether it’s anxiety about an upcoming event or frustration over a challenging task—you can begin to address these feelings constructively.
Research has shown that individuals who engage in emotion naming during stressful situations report lower levels of anxiety compared to those who do not practice this skill. By acknowledging your feelings rather than suppressing them, you create an opportunity for healthier coping mechanisms to emerge. This proactive approach not only alleviates immediate stress but also contributes to long-term emotional resilience.
Conclusion and Future Research on Emotion Naming and Amygdala Activation
In conclusion, emotion naming is a powerful tool that plays a vital role in emotional processing, regulation, and overall mental health. The intricate relationship between emotion naming and amygdala activation highlights its significance in shaping how you experience and respond to emotions. As research continues to explore this connection, there is great potential for developing innovative therapeutic approaches that leverage emotion naming as a means of enhancing emotional well-being.
Future research should focus on further elucidating the mechanisms underlying the relationship between emotion naming and brain function while exploring practical applications across various contexts—be it therapy, education, or personal development. By continuing to investigate the benefits of emotion naming, we can unlock new pathways for fostering emotional intelligence and resilience in individuals from all walks of life.
Research has shown that naming emotions can significantly reduce amygdala activation, which is crucial for emotional regulation. This concept is further explored in an article on the importance of emotional awareness and its impact on mental health. For more insights, you can read the article at Productive Patty.
FAQs
What does it mean to name emotions?
Naming emotions refers to the process of identifying and labeling one’s feelings with specific words, such as “anger,” “fear,” or “happiness.”
What is the amygdala and what role does it play in emotions?
The amygdala is a part of the brain involved in processing emotions, especially those related to fear and threat detection. It plays a key role in emotional responses and memory formation.
How does naming emotions affect amygdala activation?
Research shows that naming emotions can reduce activation in the amygdala. This means that putting feelings into words helps to regulate emotional responses and decrease the intensity of emotional reactions.
Why is reducing amygdala activation important?
Reducing amygdala activation can help lower stress and anxiety levels, improve emotional regulation, and promote better mental health by preventing overwhelming emotional responses.
Is naming emotions a technique used in therapy?
Yes, naming emotions is a common technique in therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices. It helps individuals gain awareness and control over their emotional experiences.
Can anyone practice naming emotions to improve emotional regulation?
Yes, anyone can practice naming their emotions as a simple and effective strategy to better understand and manage their feelings.
Are there scientific studies supporting the effect of naming emotions on the brain?
Yes, multiple neuroimaging studies have demonstrated that labeling emotions reduces amygdala activity and engages brain regions involved in cognitive control and emotional regulation.
Does naming emotions work for all types of emotions?
Naming emotions is generally effective for a wide range of emotions, particularly those that are intense or negative, as it helps to create psychological distance and reduce emotional intensity.
How quickly does naming emotions reduce amygdala activation?
The reduction in amygdala activation can occur rapidly, often within seconds to minutes after labeling the emotion, according to neuroimaging research.
Can naming emotions be combined with other emotional regulation strategies?
Yes, naming emotions can be combined with other techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or cognitive reframing to enhance overall emotional regulation.